The equivalent carbon content approach is used to calculate the characteristics of ferrous materials, such as steel and cast iron, that contain more than just carbon as an alloyant. This method converts the percentage of other alloying elements into a comparable carbon percentage, using a better-understood relationship between carbon and iron. This approach is commonly used in welding, heat treating, and casting cast iron.
WHAT MAKES CARBON EQUIVALENT IMPORTANT?
When two pieces of metal will be joined together via welding, such as when joining two pipes, it is crucial to understand the carbon equivalent, or CE value. Environmental factors can cause pipes to move or expand and contract. The possibility of the weld spot being a weak place is increased if one pipe is stronger than the other. Two pipes that have been joined by welding should ideally function as a single unit. The weld will either sheer or fracture if the two pieces of metal have too different of characteristics to function as a single unit.
Steel
During welding, equivalent carbon content (C.E.) is used to determine how various alloying elements affect the hardness of the steel being welded. Since hydrogen-induced cold cracking is the most frequent weld flaw in steel, this is directly tied to it, which is why it’s the most popular method for assessing weldability. Higher carbon content and other alloying elements including manganese, chromium, silicon, molybdenum, vanadium, copper, and nickel have the tendency to increase hardness while lowering weldability. However, as each of these elements has a different tendency to have an impact on the steel’s hardness and weldability, it is required to compare the hardness of two alloys created from various alloying elements in order to determine the difference in hardness between them.
According to the AWS, there is a risk of cracking in the heat-affected zone (HAZ) on flame cut edges and welds for equivalent carbon contents more than 0.40%. Although CE is rarely used in structural engineering standards, they do set a maximum percentage for several alloying elements. This custom has been around since before the CE idea even existed. This has created problems because some high strength steels are now being used that have brittle failures and a CE higher than 0.50%.

For determining the carbon equivalent value the following IIW (International Institute for Welding) formula shall be used:
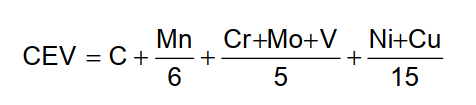
Maximum CEV based on the ladle analysis :
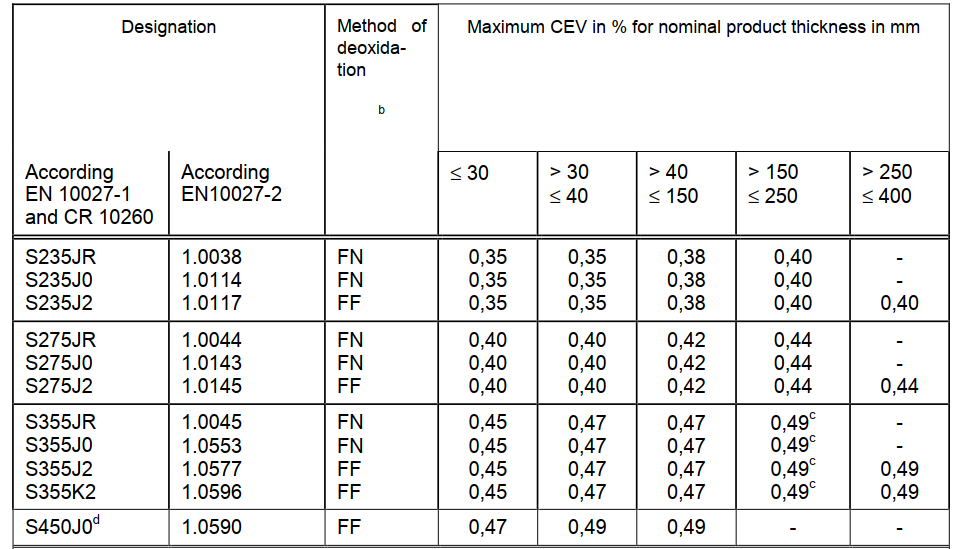
b FN = rimming steels not permitted; FF = fully killed steel
c For long products a maximum CEV of 0,54 applies.
d Applicable for long products only.
Cast Iron
To clarify how alloying materials would affect the heat treatment and casting behavior for cast iron, the equivalent carbon content (CE) idea is applied. Because it provides an approximation of the balance between austenite and graphite in the finished structure, it is employed as a predictor of strength in cast irons. There are several formulas available to calculate the CE in cast irons, which contain an increasing number of elements.
The alloy’s hypoeutectic, eutectic, or hypereutectic nature is then determined using this CE; for cast irons, the eutectic is 4.3% carbon. This is helpful for predicting the final grain structure when casting cast iron; for instance, a hypereutectic cast iron typically has a coarse grain structure and produces large flakes of kish graphite.
Additionally, as the CE rises, there is less shrinking. Various CE samples are evaluated to determine the empirical relationship between CE and hardness during the heat treatment of cast iron.
The formula of the Carbon Equivalent Value for Cast Iron:
CEV = %C + 1/3 (%Si + %P)