FORGING
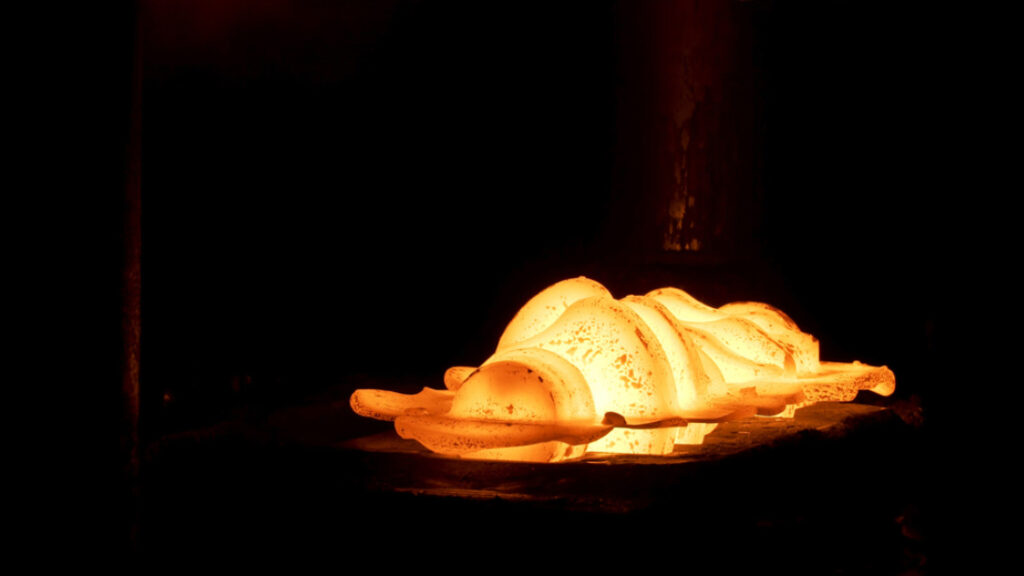

Hot Open Die Forging :
Hot open die forging is a metalworking process in which a piece of metal is heated to a high temperature and then shaped by being pounded or pressed between a series of open dies. The process is called “open die” forging because the dies (tools used to shape the metal) do not enclose the workpiece, allowing it to be shaped on all sides.In hot open die forging, the metal is heated to a temperature that is high enough to make it malleable, but not so high that it becomes brittle. The heated metal is then placed between the open dies and shaped using a hammer or a press. The force applied to the metal causes it to flow and take on the shape of the dies. Hot open die forging is typically used to produce parts with complex shapes and large sizes, such as aircraft landing gear and hydraulic cylinders. The process is known for its ability to produce parts with high strength and good surface finish. It is also a cost-effective method for producing high volumes of parts, as it allows for a high degree of material utilization and produces minimal waste.
Hot Closed Die Forging
Hot closed die forging is a metalworking process in which a piece of metal is heated to a high temperature and then shaped by being pounded or pressed between a series of dies that enclose the workpiece. The process is called “closed die” forging because the dies completely enclose the workpiece, allowing it to be shaped on all sides.
In hot closed die forging, the metal is heated to a temperature that is high enough to make it malleable, but not so high that it becomes brittle. The heated metal is then placed in a die cavity and shaped using a hammer or a press. The force applied to the metal causes it to flow and take on the shape of the die cavity.
Hot closed die forging is typically used to produce parts with complex shapes and high precision, such as automotive gears and aerospace components. The process is known for its ability to produce parts with high strength and good surface finish. It is also a cost-effective method for producing small volumes of parts, as it allows for a high degree of material utilization and produces minimal waste.
Cold Closed Die Forging
Cold closed die forging is a metalworking process in which a piece of metal is shaped by being pounded or pressed between a series of dies that enclose the workpiece, while the metal is at or near room temperature. The process is called “closed die” forging because the dies completely enclose the workpiece, allowing it to be shaped on all sides.
In cold closed die forging, the metal is placed in a die cavity and shaped using a hammer or a press. The force applied to the metal causes it to flow and take on the shape of the die cavity. The metal is not heated before forging, so it remains at or near room temperature throughout the process.
Cold closed die forging is typically used to produce parts with complex shapes and high precision, such as automotive gears and aerospace components. The process is known for its ability to produce parts with high strength and good surface finish. It is also a cost-effective method for producing small volumes of parts, as it allows for a high degree of material utilization and produces minimal waste. Cold closed die forging is often used to produce parts from materials that are difficult to forge at high temperatures, such as high-strength steel alloys.
Cold Heading and Upsetting
Cold heading and upsetting are metalworking processes that are used to shape and form metal parts by applying pressure at room temperature.
Cold heading is a process in which a piece of metal is shaped by being pounded or pressed into a die using a punch or a press. The metal is not heated before forging, so it remains at or near room temperature throughout the process. Cold heading is often used to produce parts with precise tolerances and smooth surface finishes, such as screws, bolts, and nails.
Upsetting is a process in which a piece of metal is lengthened and thickened by being pounded or pressed. The metal is not heated before forging, so it remains at or near room temperature throughout the process. Upsetting is often used to produce parts with increased strength and reduced weight, such as fasteners and shafts.
Both cold heading and upsetting are cost-effective methods for producing small volumes of parts, as they allow for a high degree of material utilization and produce minimal waste. They are also well-suited for producing parts with high strength and good surface finish.
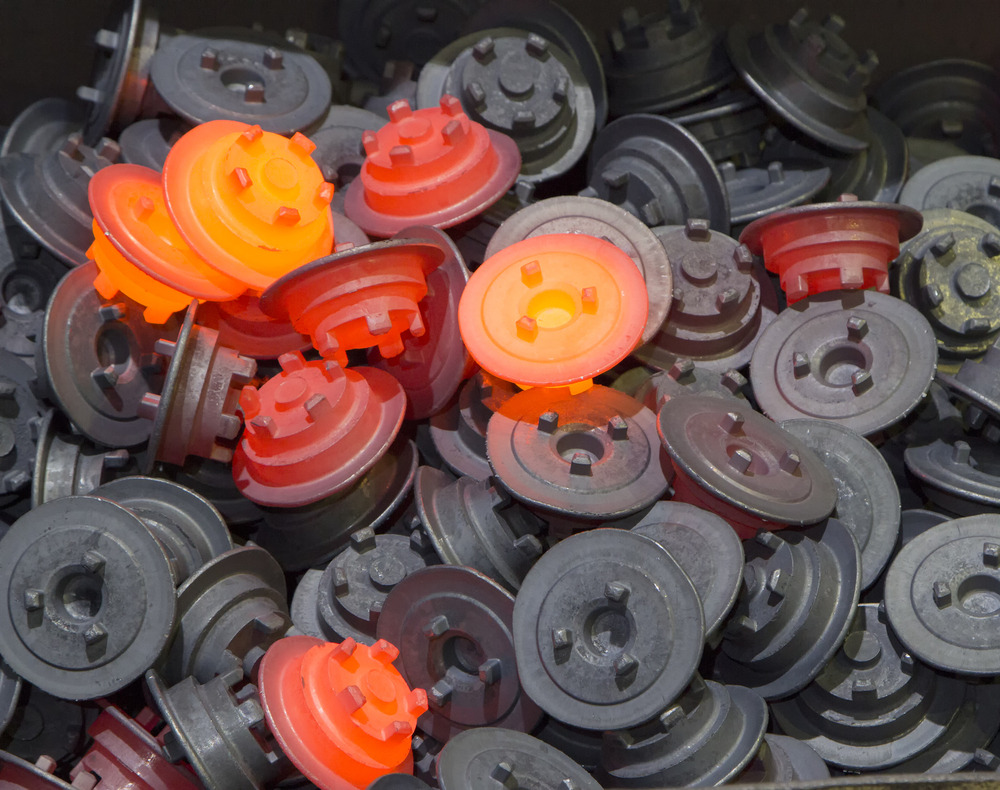

ROLLING
Cold Shape Rolling
Cold shape rolling is a metalworking process in which a piece of metal is shaped by being passed through a set of rolls at room temperature. The process is also known as cold rolling.
In cold shape rolling, the metal is placed between a set of rolls, which are powered to rotate in opposite directions. The rolls apply pressure to the metal, causing it to flow and take on the shape of the rolls. The metal is not heated before rolling, so it remains at or near room temperature throughout the process.
Cold shape rolling is often used to produce parts with precise dimensions and good surface finishes, such as sheet metal and wire. The process is known for its ability to produce parts with high strength and good dimensional accuracy. It is also a cost-effective method for producing high volumes of parts, as it allows for a high degree of material utilization and produces minimal waste.
Hot Shape Rolling
Hot shape rolling is a metalworking process in which a piece of metal is shaped by being passed through a set of rolls at high temperatures. The process is also known as hot rolling.
In hot shape rolling, the metal is heated to a temperature that is high enough to make it malleable, but not so high that it becomes brittle. The heated metal is then placed between a set of rolls, which are powered to rotate in opposite directions. The rolls apply pressure to the metal, causing it to flow and take on the shape of the rolls.
Hot shape rolling is often used to produce parts with complex shapes and large sizes, such as beams, plates, and structural shapes. The process is known for its ability to produce parts with high strength and good surface finish. It is also a cost-effective method for producing high volumes of parts, as it allows for a high degree of material utilization and produces minimal waste.
Swaging
Swaging is a metalworking process in which a piece of metal is shaped by being pounded or pressed with a die or a series of dies. The process is similar to forging, but it is typically performed at room temperature and with greater precision.
In swaging, a piece of metal is placed in a die cavity and shaped using a hammer or a press. The force applied to the metal causes it to flow and take on the shape of the die cavity. The metal is not heated before swaging, so it remains at or near room temperature throughout the process.
Swaging is often used to produce parts with precise dimensions and smooth surface finishes, such as tubes, rods, and wire. The process is known for its ability to produce parts with high strength and good dimensional accuracy. It is also a cost-effective method for producing small volumes of parts, as it allows for a high degree of material utilization and produces minimal waste.
USEFUL INFO
Important EN ISO Forging Standard List

