Modulus Metal is a company that provides a range of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining services. The company is equipped to perform all types of CNC machining processes, including milling, turning, drilling, grinding, and EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining). Modulus Metal is capable of producing parts with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
In addition to offering a range of CNC machining processes, Modulus Metal is also available to perform all CNC axis, from 1 to 5. This means that the company is equipped to produce parts with complex geometries and tight tolerances using advanced CNC machines. Modulus Metal is known for its ability to produce high-quality parts with precise dimensional accuracy and smooth surface finishes. The company is well-suited for mass production and is able to produce a wide range of parts with high precision and efficiency.
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a manufacturing process in which machine tools are controlled using computer programs. There are several types of operations that can be performed using CNC machining, including:
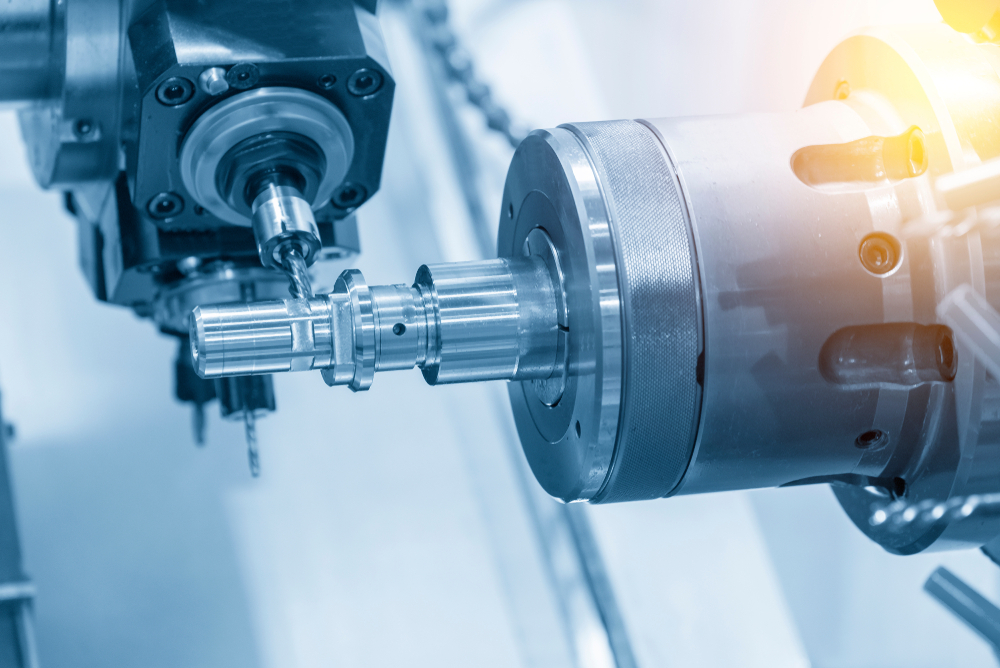
Milling: Milling is a process in which a rotating cutter is used to remove material from the surface of a workpiece. In CNC milling, the workpiece is mounted on a bed or table and moved under a rotating cutter, which removes material to create the desired shape. CNC milling machines are equipped with multiple axes, which allows for the production of parts with complex geometries. Milling can be performed on a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
Turning: Turning is a process in which a workpiece is rotated against a cutting tool to produce cylindrical shapes. In CNC turning, the workpiece is mounted on a spindle and rotated while a cutting tool is applied to the surface to remove material. CNC turning machines are equipped with multiple axes, which allows for the production of parts with complex geometries. Turning can be performed on a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
Drilling: Drilling is a process in which a rotating cutter is used to create holes in a workpiece. In CNC drilling, the workpiece is mounted on a bed or table and a rotating cutter is used to create holes of precise sizes and depths. CNC drilling machines are equipped with multiple axes, which allows for the production of parts with complex geometries. Drilling can be performed on a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
Grinding: Grinding is a process in which a rotating abrasive wheel is used to remove material from the surface of a workpiece. In CNC grinding, the workpiece is mounted on a bed or table and moved under a rotating abrasive wheel, which removes material to create the desired shape. CNC grinding machines are equipped with multiple axes, which allows for the production of parts with complex geometries. Grinding can be performed on a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining): EDM is a process in which a controlled electrical spark is used to remove material from the surface of a workpiece. In CNC EDM, a wire or electrode is used to generate an electrical spark that removes material from the workpiece. CNC EDM machines are equipped with multiple axes, which allows for the production of parts with complex geometries. EDM can be performed on a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
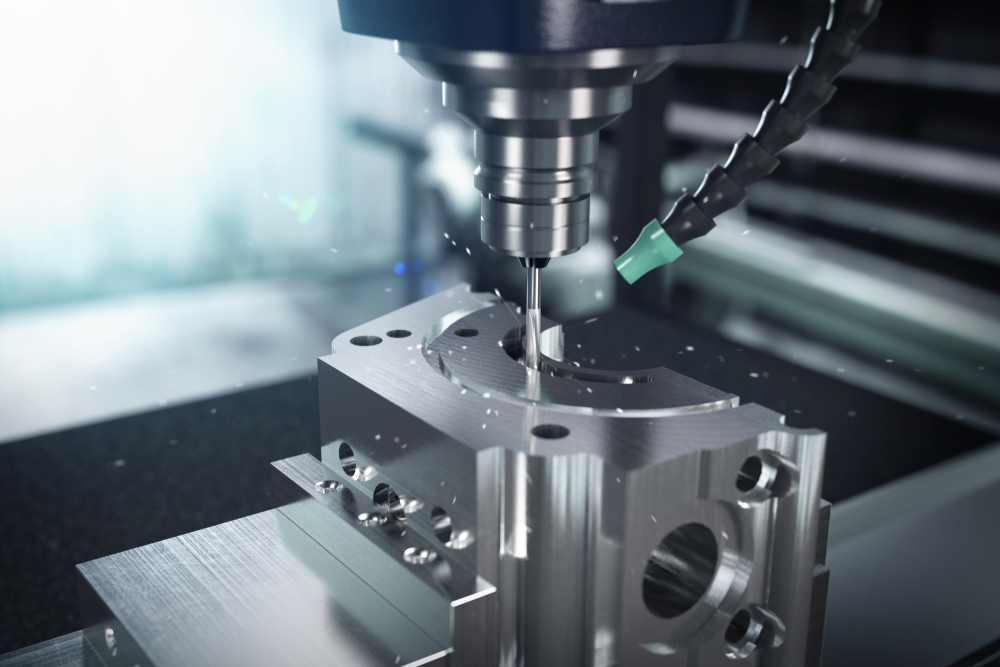

Boring :
CNC boring is a metalworking process in which a rotating cutting tool is used to create a hole with a precise diameter and depth in a workpiece. The process is performed using a CNC (Computer Numerical Control) boring machine, which is equipped with a rotating cutting tool and is controlled using computer programs.
In CNC boring, the workpiece is mounted on a bed or table and held in place using fixtures. The cutting tool is mounted on a spindle and is guided along precise paths to create the desired hole. The depth and diameter of the hole are controlled using the computer program, which specifies the movements of the cutting tool.
CNC boring is a precise and efficient process that is used to produce holes with high dimensional accuracy and smooth surface finishes. It is often used to produce large or deep holes, or holes with complex geometries, such as tapered or stepped holes. The process is well-suited for mass production and can be used to produce a wide range of parts with high precision and tight tolerances.
Parting:
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) parting is a metalworking process in which a rotating cutting tool is used to separate a workpiece into two or more parts. The process is performed using a CNC parting machine, which is equipped with a rotating cutting tool and is controlled using computer programs.
In CNC parting, the workpiece is mounted on a bed or table and held in place using fixtures. The cutting tool is mounted on a spindle and is guided along precise paths to separate the workpiece into the desired parts. The dimensions of the parts are controlled using the computer program, which specifies the movements of the cutting tool.
CNC parting is a precise and efficient process that is used to produce parts with high dimensional accuracy and smooth surface finishes. It is often used to produce parts with complex geometries or tight tolerances, such as gears and shafts. The process is well-suited for mass production and can be used to produce a wide range of parts with high precision.
Reaming:
Reaming is a metalworking process in which a rotating cutting tool is used to enlarge and smooth a hole that has already been drilled or bored. The process is performed using a reaming tool, which is a specialized cutting tool with multiple cutting edges.
In reaming, the workpiece is held in place using a chuck or a fixture, and the reaming tool is inserted into the hole. The tool is rotated and advanced into the hole, removing a small amount of material to enlarge and smooth the surface. Reaming is typically used to produce holes with high dimensional accuracy and smooth finishes.
Reaming is a precise and efficient process that is used to produce holes with high tolerances and smooth surface finishes. It is often used to produce holes with precise diameters and accurate straightness, such as those used for bearings or shafts. The process is well-suited for mass production and can be used to produce a wide range of parts with high precision.
Broaching:
Broaching is a metalworking process in which a series of cutting teeth are used to shape or finish a workpiece. The process is performed using a broach, which is a specialized cutting tool with a series of teeth arranged in a linear or circular pattern.
In broaching, the workpiece is held in place using a chuck or a fixture, and the broach is inserted into the workpiece. The broach is then advanced through the workpiece, removing material to create the desired shape or finish. Broaching is typically used to produce parts with complex shapes or precise tolerances, such as gears or splines.
Broaching is a precise and efficient process that is used to produce parts with high dimensional accuracy and smooth surface finishes. It is often used to produce parts with complex geometries or tight tolerances, such as gears and splines. The process is well-suited for mass production and can be used to produce a wide range of parts with high precision.
Planning, Shaping, Slotting:
Planning, shaping, and slotting are metalworking processes that are used to shape and finish a workpiece by removing material using a cutting tool.
- Planning: Planning is a process in which a workpiece is shaped by being moved across a stationary cutting tool. The cutting tool removes material from the surface of the workpiece to create the desired shape. Planning is often used to produce flat or slightly contoured surfaces with high precision and smooth finishes.
- Shaping: Shaping is a process in which a workpiece is shaped by being moved under a reciprocating cutting tool. The cutting tool removes material from the surface of the workpiece to create the desired shape. Shaping is often used to produce complex shapes and contours with high precision and smooth finishes.
- Slotting: Slotting is a process in which a workpiece is shaped by being moved under a rotating cutting tool that is able to move vertically. The cutting tool removes material from the surface of the workpiece to create slots or channels with precise dimensions and smooth finishes. Slotting is often used to produce parts with precise slots or channels, such as gears or splines.
Planning, shaping, and slotting are precise and efficient processes that are used to produce parts with high dimensional accuracy and smooth surface finishes. They are often used to produce parts with complex geometries or tight tolerances, such as gears and splines. These processes are well-suited for mass production and can be used to produce a wide range of parts with high precision.
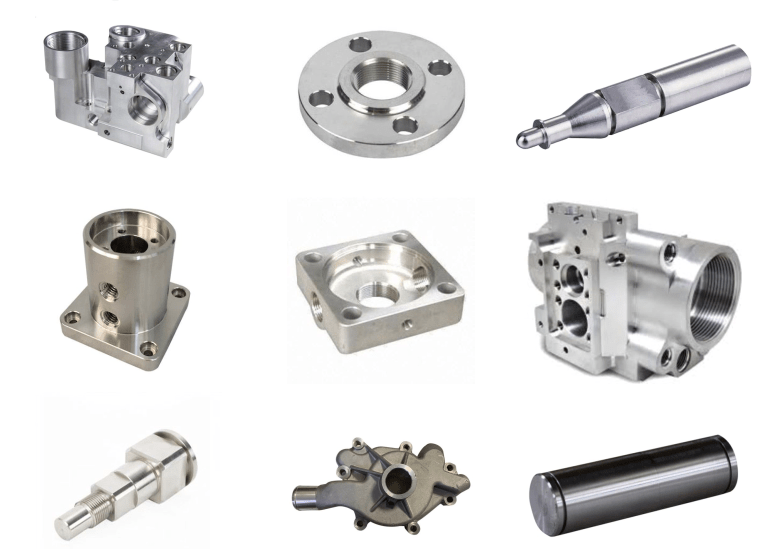
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are classified according to the number of axes that they are equipped with. The number of axes refers to the number of directions in which the machine is able to move the cutting tool.
- Single-axis CNC machines: Single-axis CNC machines are equipped with one axis of motion, which allows them to move the cutting tool along a single direction. Single-axis CNC machines are typically used for simple machining operations, such as drilling or turning.
- Two-axis CNC machines: Two-axis CNC machines are equipped with two axes of motion, which allows them to move the cutting tool along two directions. Two-axis CNC machines are typically used for more complex machining operations, such as milling or grinding.
- Three-axis CNC machines: Three-axis CNC machines are equipped with three axes of motion, which allows them to move the cutting tool along three directions. Three-axis CNC machines are commonly used for a wide range of machining operations, such as milling, drilling, and turning.
- Four-axis CNC machines: Four-axis CNC machines are equipped with four axes of motion, which allows them to move the cutting tool along four directions. Four-axis CNC machines are typically used for more complex machining operations, such as milling and grinding.
- Five-axis CNC machines: Five-axis CNC machines are equipped with five axes of motion, which allows them to move the cutting tool along five directions. Five-axis CNC machines are used for advanced machining operations, such as milling and grinding, and are capable of producing parts with complex geometries.
USEFUL INFO
List of ISO Standards for Screw Threads

