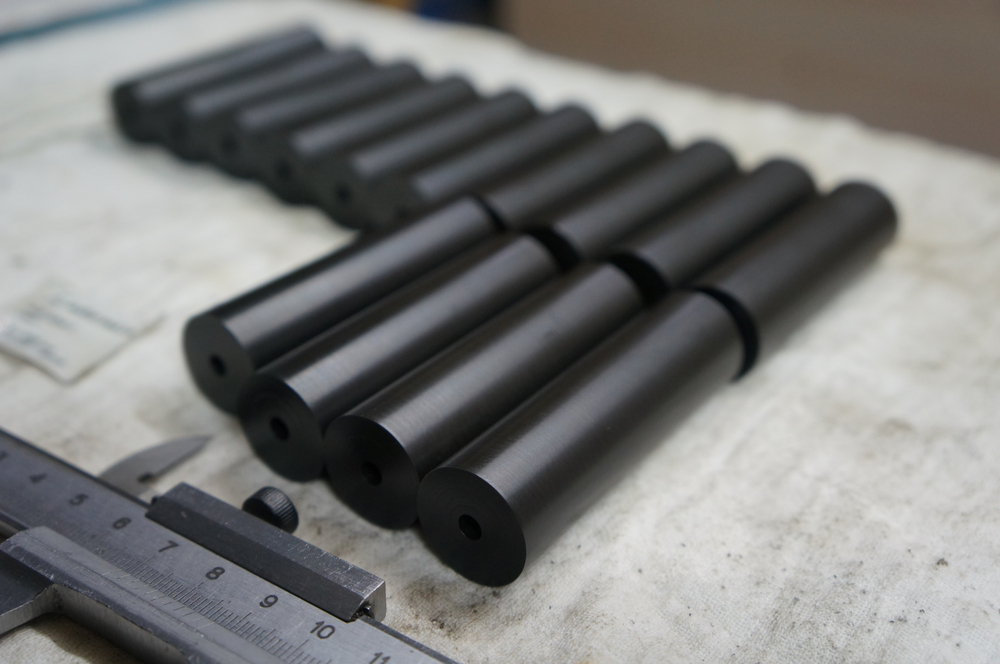
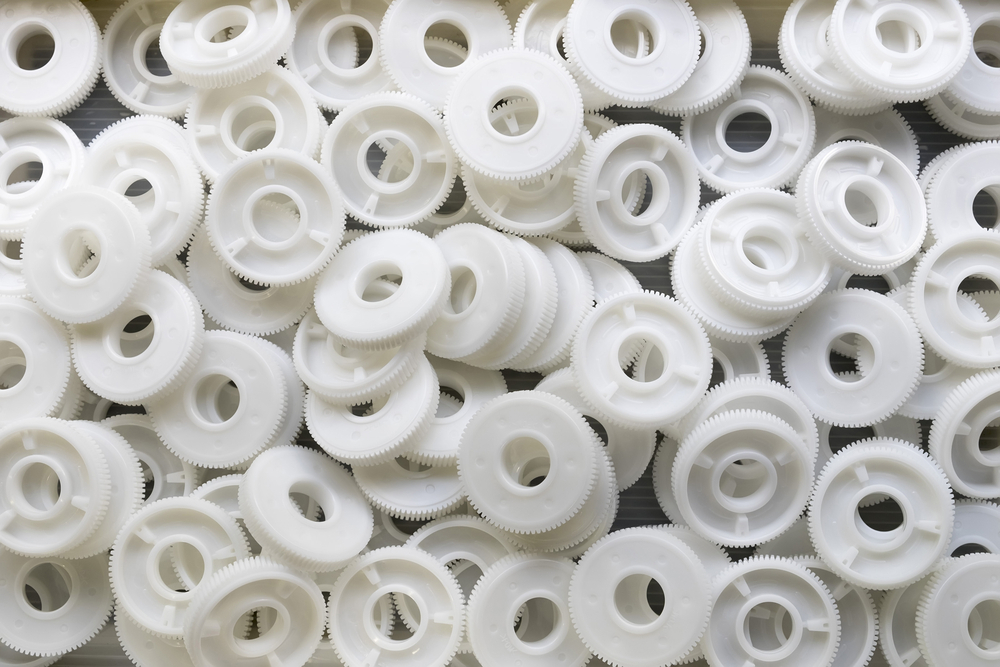
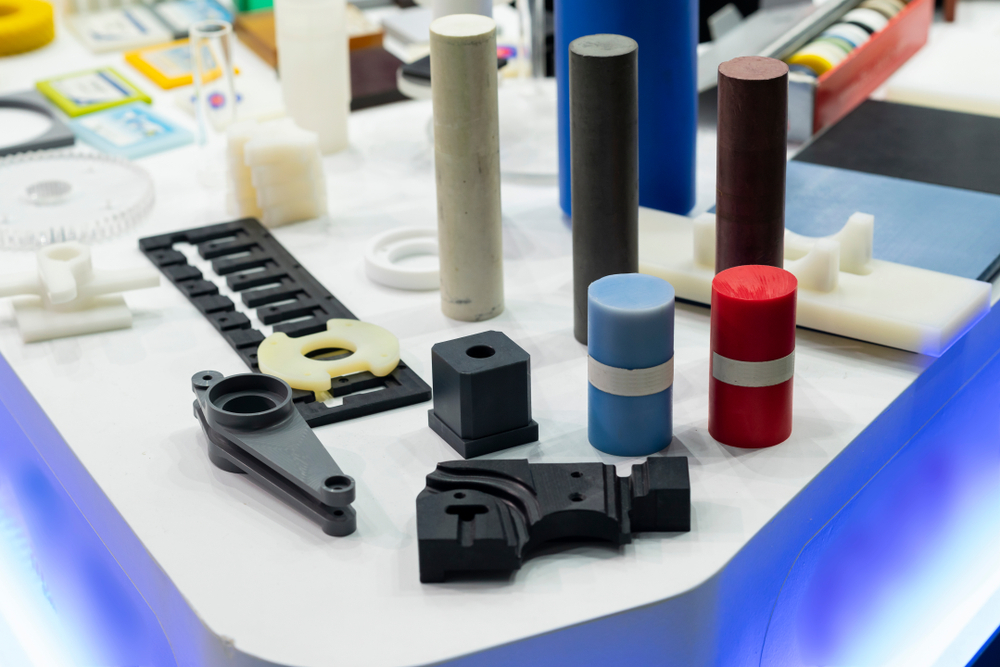
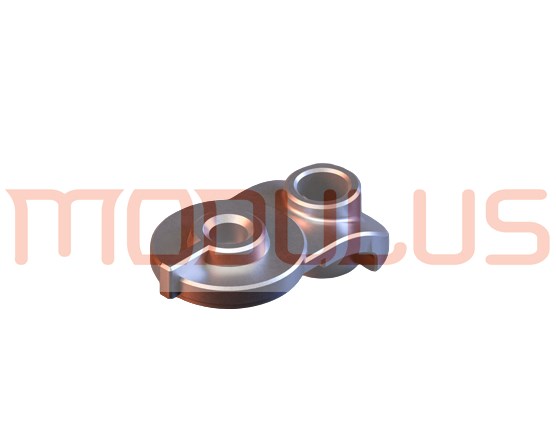
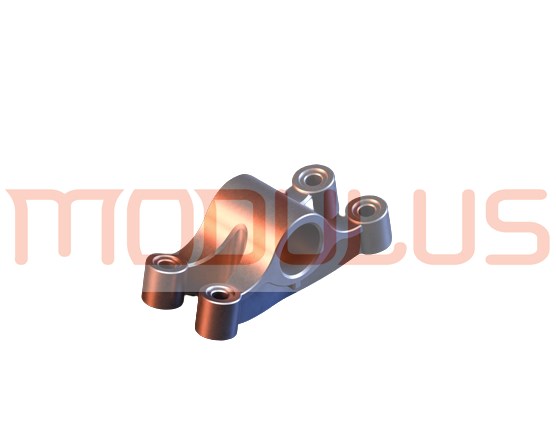
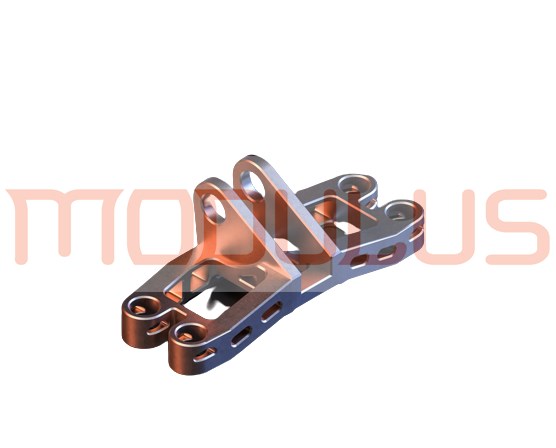
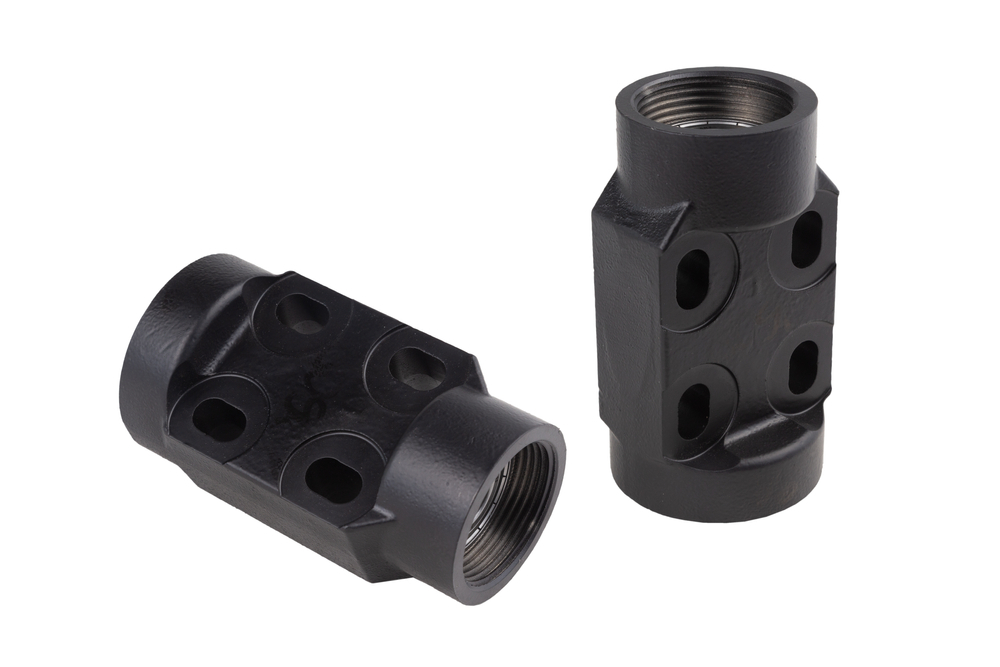
Modulus Metal is a leading provider of CNC machining services for Polyamide (Nylon) in Turkey. Our team of skilled professionals utilizes state-of-the-art CNC machines to produce high-quality Nylon parts with precision and accuracy. We offer Nylon CNC machining services for a wide range of applications, and we are committed to delivering the best results to our clients.
Types of Polyamide (Nylon):
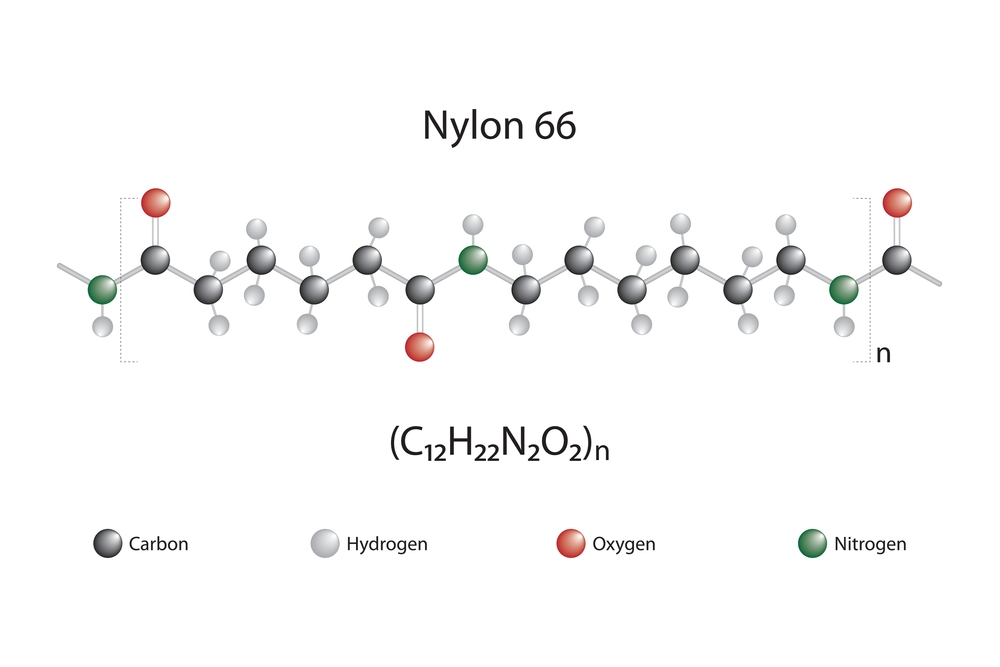
Polyamide is a group of polymers that contains amide groups (-CO-NH-) in their molecular structure. There are various types of Nylon, each with its own unique properties and characteristics. Some of the most common types of Nylon we work with include:
- Nylon 6: This type of Nylon is a semi-crystalline material that offers high strength, stiffness, and toughness. It is suitable for applications that require high mechanical strength and resistance to wear and abrasion.
- Nylon 6/6: This type of Nylon is a crystalline material that offers excellent mechanical properties and chemical resistance. It is suitable for applications that require high strength, stiffness, and dimensional stability.
- Nylon 11: This type of Nylon is a semi-crystalline material that offers excellent impact resistance and flexibility. It is suitable for applications that require resistance to chemicals, abrasion, and impact.
Colors:
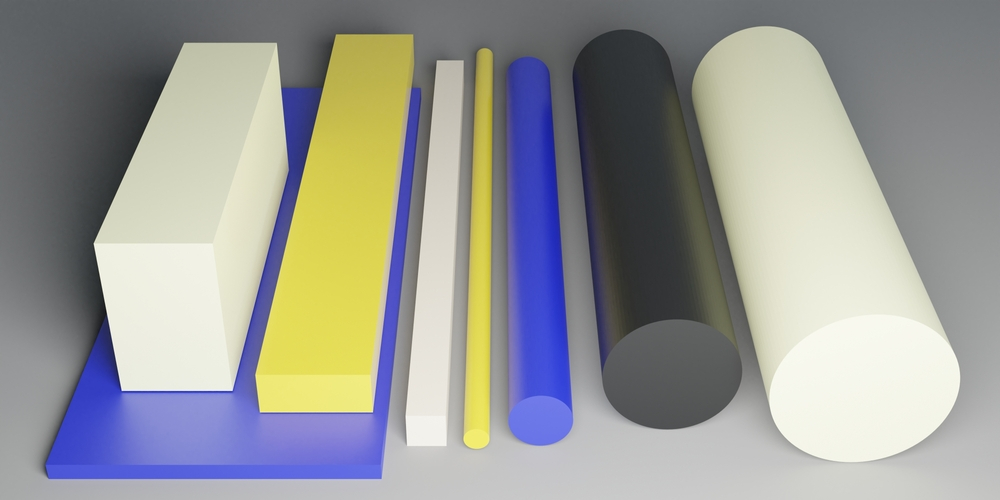
Nylon is available in a variety of colors, including natural (white), black, blue, green, red, and yellow. The color of the Nylon does not affect its mechanical properties, but it can provide aesthetic appeal or help with product identification.
Physical and mechanical properties:
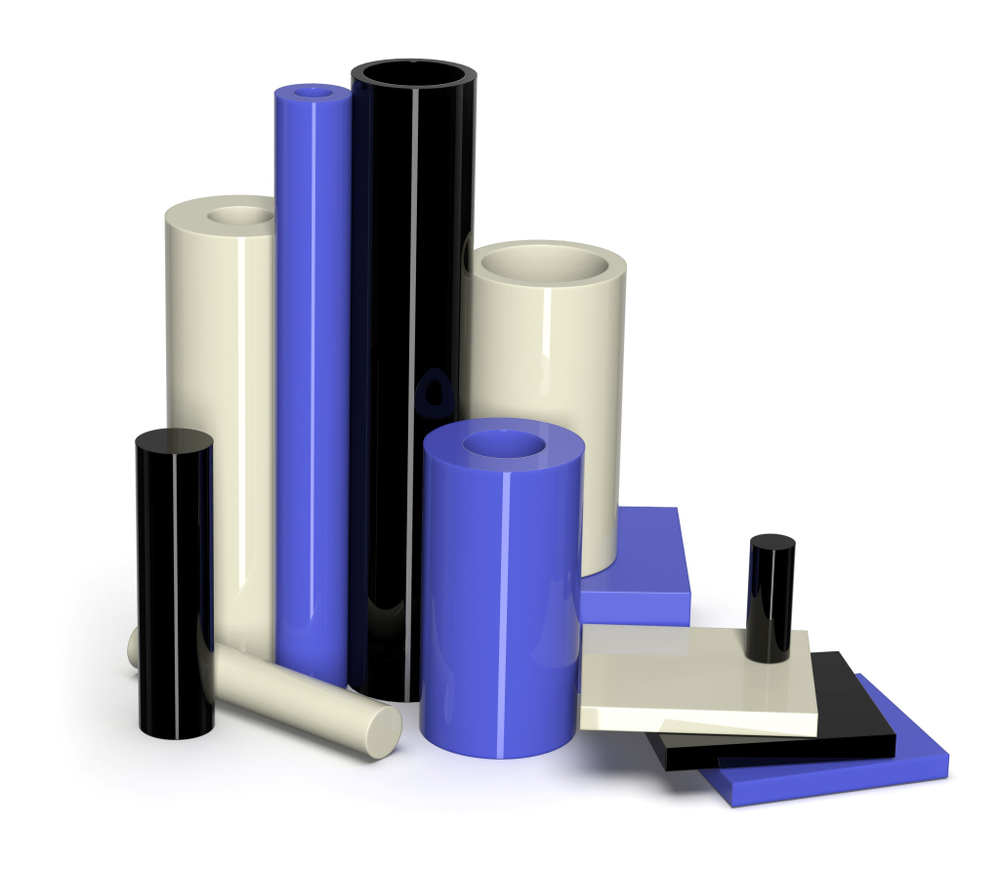

Nylon (Polyamide) has excellent physical and mechanical properties, including high strength, stiffness, toughness, and chemical resistance. Some of its key properties are:
- Melting temperature: The melting temperature of Nylon ranges from 220°C to 265°C, depending on the type of Nylon.
- Hardness: Nylon has a hardness of around 70 to 80 on the Rockwell scale, making it relatively hard and durable.
- Tensile strength: The tensile strength of Nylon ranges from 50 to 150 MPa, depending on the type of Nylon.
- Flexural modulus: Nylon has a flexural modulus of around 1,000 to 3,000 MPa, making it relatively stiff and strong.
- Coefficient of friction: Nylon has a low coefficient of friction, making it suitable for applications that require low friction and wear resistance.
- Water absorption: Nylon has a high water absorption rate, making it suitable for applications that require good dimensional stability and resistance to moisture.
Types of machining:
At Modulus Metal, we use various types of machining techniques to produce high-quality Nylon parts, including:
- Turning: Turning is a process in which a cutting tool removes material from the surface of a rotating Nylon workpiece to produce a cylindrical shape. Turning is ideal for producing parts with round shapes, such as shafts, rods, and bushings.
- Milling: Milling is a process in which a rotating cutting tool removes material from a Nylon workpiece to produce a flat or contoured surface. Milling is ideal for producing complex shapes, such as gears, brackets, and housings.
- Drilling: Drilling is a process in which a rotating cutting tool removes material from a Nylon workpiece to produce a round hole. Drilling is ideal for producing holes with accurate diameters and depths.
- Threading: Threading is a process in which a cutting tool removes material from a Nylon workpiece to produce a screw thread. Threading is ideal for producing parts that require screw connections, such as bolts, nuts, and threaded rods.
Examples of products:
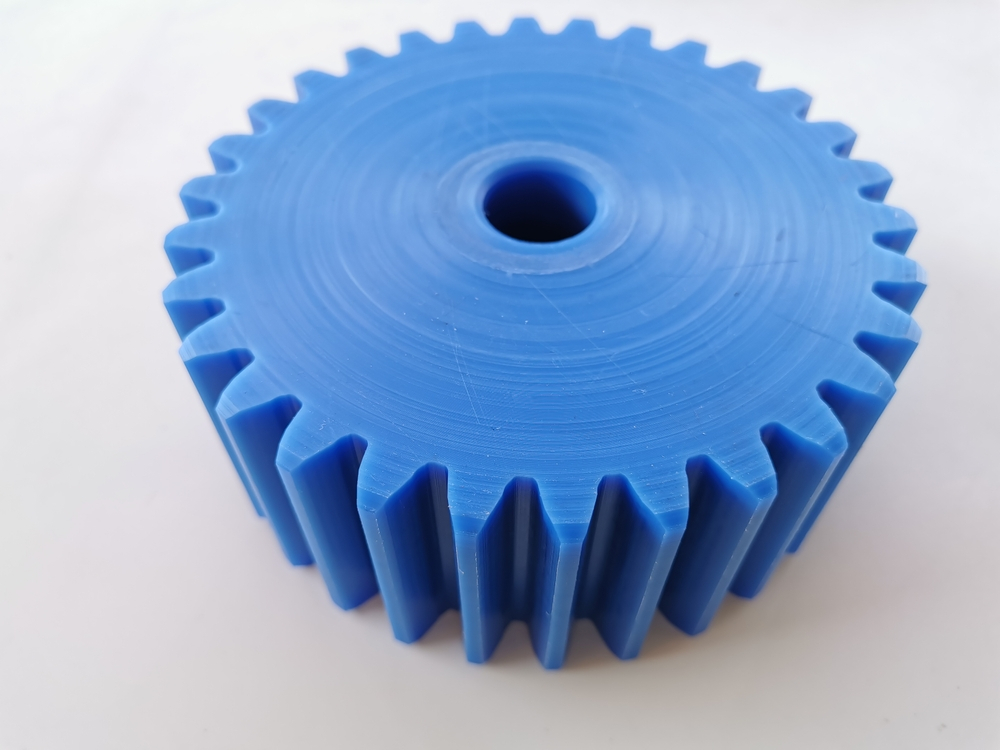
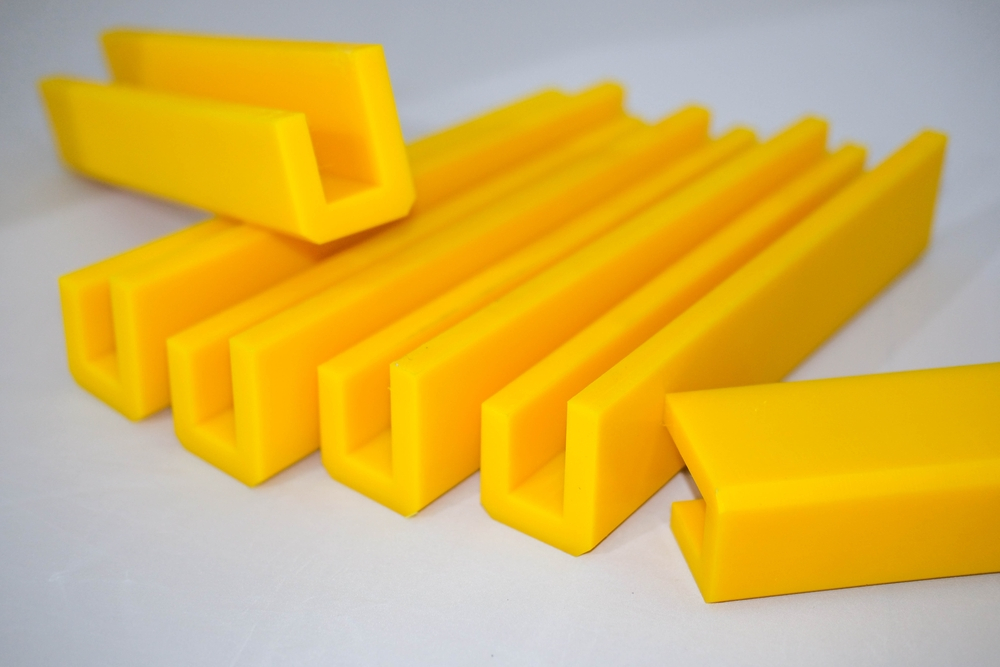

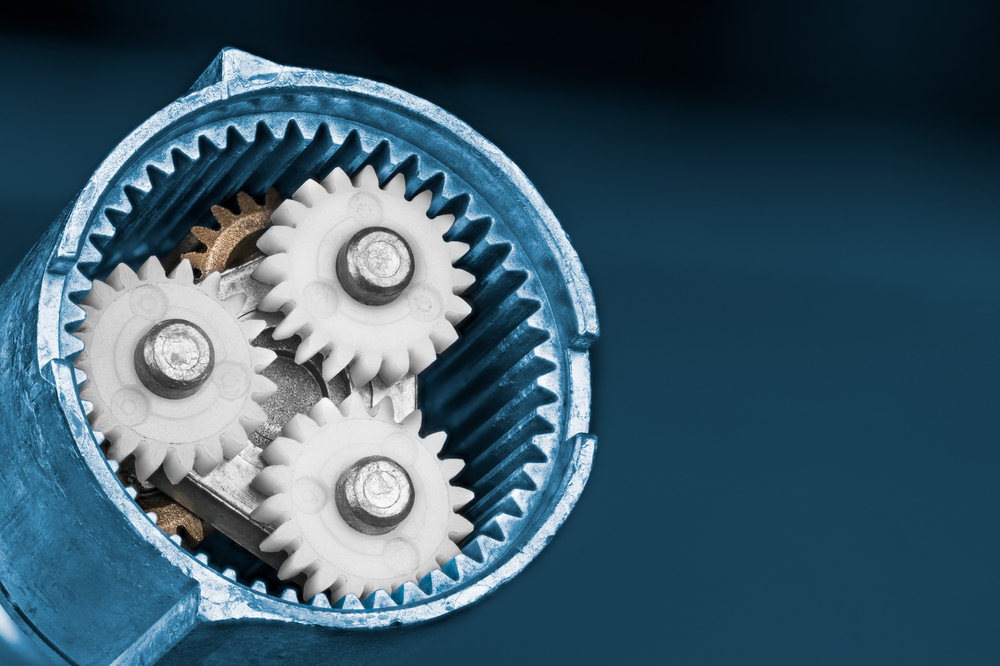
We provide CNC machining services for a wide range of Nylon parts, including:
- Gears and bearings: Nylon’s excellent wear resistance and low friction properties make it an ideal material for producing gears and bearings used in various industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical.
- Structural components: Nylon’s high strength and stiffness properties make it suitable for producing structural components used in the construction of machines, equipment, and devices.
- Electrical components: Nylon’s excellent dielectric properties and resistance to heat and chemicals make it an ideal material for producing electrical components such as insulators, connectors, and housings.
- Automotive parts: Nylon’s excellent impact resistance, toughness, and wear resistance make it an ideal material for producing automotive parts such as fuel system components, engine covers, and brake parts.
- Medical devices: Nylon’s biocompatibility and resistance to chemicals and sterilization make it an ideal material for producing medical devices such as surgical instruments, implantable devices, and prosthetics.
At Modulus Metal, we are committed to providing high-quality Nylon CNC machining services to meet the unique needs of our clients. Our team of experts works closely with clients to ensure that every part meets their exact specifications, and we use only the best materials and equipment to deliver exceptional results. Contact us today to learn more about our Polyamide (Nylon) CNC machining services.