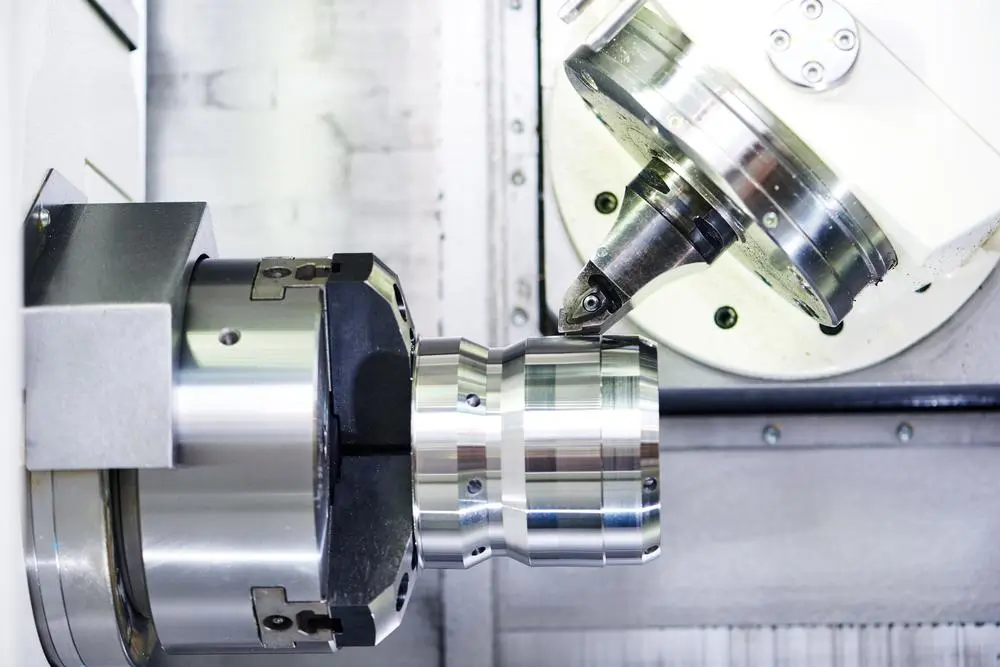
C-axis turning-milling is a highly advanced CNC machining process that combines the capabilities of a traditional lathe with those of a milling machine. This synergistic approach allows for the production of complex parts with intricate geometries in a single setup, significantly reducing production time and increasing precision. This detailed guide will delve into the logic of C-axis turning-milling, the applicable shapes and geometries, and highlight Modulus Metal, a Turkish company excelling in these services for international customers.
The Logic of C-Axis Turning-Milling
At its core, C-axis turning-milling leverages the rotational movement of the workpiece (the C-axis) in conjunction with linear movements of cutting tools (X and Z axes for turning, and often Y-axis for additional milling capabilities).
Traditional Lathe Limitations:
A conventional CNC lathe primarily operates with two axes:
- X-axis: Controls the tool movement radially towards or away from the workpiece centerline.
- Z-axis: Controls the tool movement axially along the workpiece.
This setup is excellent for creating cylindrical features, such as shafts, bores, and tapers. However, for features that are not concentric or radial (like flats, holes off-center, or milled pockets on the circumference), the workpiece would typically need to be transferred to a separate milling machine, leading to multiple setups, potential for error, and increased lead times.
The C-Axis Advantage:
The introduction of the C-axis transforms a lathe into a powerful “mill-turn” machine. The C-axis refers to the controlled rotational movement of the main spindle (and thus the workpiece). Instead of continuous high-speed rotation for turning, the C-axis allows for:
- Precise Angular Positioning (Indexing): The C-axis can precisely stop and hold the workpiece at specific angular positions. This enables milling, drilling, and tapping operations at various orientations around the circumference of the part.
- Synchronized Rotation (Contouring): For more complex milling operations, the C-axis can rotate simultaneously and in synchronization with the X, Y, and Z axes. This allows for continuous contouring, helical milling, and the creation of intricate shapes on the part’s rotational surface.
Live Tooling: The Key Enabler
The C-axis is almost always combined with “live tooling.” Live tools are motorized tools mounted in the machine’s turret that can rotate independently, functioning like miniature milling spindles. These tools can hold end mills, drills, taps, and other rotary cutting tools. Without live tooling, the C-axis would only be useful for indexing and drilling simple, axially aligned holes. With live tooling, the possibilities become vast.
How it Works (Simplified):
Imagine you have a cylindrical part and need to drill a hole off-center on its face, and then mill a keyway on its side.
Traditional Approach:
- Turn the part on a lathe to achieve the cylindrical form.
- Remove the part from the lathe.
- Set up the part on a milling machine, carefully aligning it to drill the off-center hole.
- Re-fixture the part (or rotate the rotary table if available) to mill the keyway. This involves multiple setups, increased risk of misalignment, and extended lead times.
C-Axis Turning-Milling Approach:
- The part is chucked in the mill-turn machine.
- Basic turning operations are performed.
- For the off-center hole, the C-axis precisely indexes the workpiece to the desired angular position. A live drill bit (mounted on a live tool) then moves in the X and Z axes to drill the hole.
- For the keyway, the C-axis might either index the part and a live end mill cuts in the X-Z plane (if it’s a simple slot), or for a contoured keyway, the C-axis rotates in synchronization with the live end mill’s X and Z movements to mill the feature. All this happens without removing the part from the machine.
This single-setup capability is what makes C-axis turning-milling incredibly efficient and precise.
Applicable Shapes and Geometries
C-axis turning-milling opens up a world of possibilities for complex part geometries. It excels in producing parts that require a combination of turned and milled features. Here are some examples of applicable shapes and geometries:
- Parts with Off-Center Holes: Drilling, boring, or tapping holes that are not coaxial with the main turned diameter, either on the face or radially on the circumference.
- Keyways and Slots: Milling straight or curved keyways, slots, or grooves on the cylindrical surface or face of a part.
- Flats and Hexes: Machining flats, hexes, or other polygonal shapes on a turned diameter.
- Irregular Contours and Pockets: Creating complex, non-circular contours, pockets, or profiles on the face or periphery of the workpiece. This includes cam profiles, intricate patterns, or sculptural elements.
- Thread Milling: While turning can cut external and internal threads, C-axis milling with live tools allows for thread milling, which can be advantageous for large threads, harder materials, or when tighter tolerances are required.
- Angled Features: With the ability to precisely orient the part, angled holes, slots, or surfaces can be machined. Some advanced mill-turn machines also incorporate a Y-axis, further expanding capabilities for features off the center line.
- Interrupted Cuts: Creating features that break the continuous cylindrical form, such as windows, cutouts, or channels.
- Medical Implants and Aerospace Components: These industries often require highly complex, multi-featured parts with tight tolerances, making C-axis machining ideal.
- Hydraulic Manifolds and Valve Bodies: Parts with numerous drilled and milled passages that intersect at various angles.
In essence, any part that traditionally required multiple setups on both a lathe and a milling machine can often be consolidated into a single operation with C-axis turning-milling, leading to superior accuracy, better surface finish, and significantly reduced lead times.
Modulus Metal: A Leader in C-Axis Machining Services in Türkiye
When seeking high-precision C-axis turning-milling services, particularly for export, Modulus Metal in Turkey stands out as a reliable and capable partner. Modulus Metal offers comprehensive manufacturing services, including advanced CNC machining (turning, milling, and 5-axis), with a strong focus on dimensional precision, material integrity, and process reliability.
Key Strengths of Modulus Metal in C-Axis Machining and Export:
- Advanced CNC Machining Capabilities: Modulus Metal explicitly lists “CNC machining (turning, milling, 5-axis)” among their services, indicating they possess the necessary equipment and expertise for complex mill-turn operations, including those utilizing C-axis functionality. Their capacity for 5-axis machining further suggests they handle highly intricate geometries.
- Multidisciplinary Engineering Team: Their projects are managed by a team of mechanical, metallurgical, and industrial engineers. This expertise is crucial for interpreting complex C-axis machining requirements, optimizing tool paths, and ensuring material suitability for demanding applications. They are proficient in interpreting GD&T symbols and all aspects of technical drawings.
- Quality Control and Compliance: Modulus Metal emphasizes full compliance with international standards such as ISO, EN, ASTM, and DIN. This commitment to quality is vital for export markets where stringent standards are non-negotiable. They implement robust inspection and process control measures.
- Proven Track Record in Export: Modulus Metal has a demonstrated history of exporting fully finished and quality-controlled components to demanding customers in Germany, France, Italy, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, the United States, Canada, and other global markets. This experience is critical for navigating international logistics, customs, and customer expectations.
- Reliable Lead Times and Technical Expertise: For international clients, consistent lead times and strong technical support are paramount. Modulus Metal’s focus on these areas makes them an attractive partner.
- Diverse Industry Experience: They supply a wide range of industries, including automotive (engine brackets, transmission housings), railway (coupler yokes, bogie side brackets), truck and trailer (fifth wheel couplings), and energy (turbine casings, generator housing panels). This broad experience indicates their versatility and capability to handle diverse C-axis machining projects across various material types and part complexities.
- Full Ownership of Projects: From technical file evaluation to production, inspection, and delivery, Modulus Metal takes full ownership, providing a streamlined experience for clients.
For businesses globally looking to outsource complex C-axis turning-milling requirements, Modulus Metal in Turkey offers a compelling combination of advanced technical capabilities, rigorous quality control, and extensive export experience, ensuring efficient and high-quality production of even the most challenging components.
By understanding the underlying principles of C-axis turning-milling and recognizing the capabilities of specialized manufacturers like Modulus Metal, companies can unlock new levels of precision, efficiency, and complexity in their machined parts.